#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
struct data {
char name[64];
};
struct fp {
int (*fp)();
};
void winner()
{
printf("level passed\n");
}
void nowinner()
{
printf("level has not been passed\n");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
struct data *d;
struct fp *f;
d = malloc(sizeof(struct data));
f = malloc(sizeof(struct fp));
f->fp = nowinner;
printf("data is at %p, fp is at %p\n", d, f);
strcpy(d->name, argv[1]);
f->fp();
}
모든 보호기법이 없다.
ASLR도 꺼야된다.


main+16을 실행 후 main+21에서 eax 값을 확인해 보자 -> malloc 반환값이 eax에 들어가 있을 것이다.

일단 argv[1]에는 AAAA 문자열을 넣는다.
main+21에 도착 후 eax 값을 확인해 보면 0으로 초기화되어있다. -> 아직 값을 안 넣었기 때문
malloc 반환값은 heap에 할당된 영역 주소를 반환하는데 데이터가 입력되는 payload 주소를 반환한다.
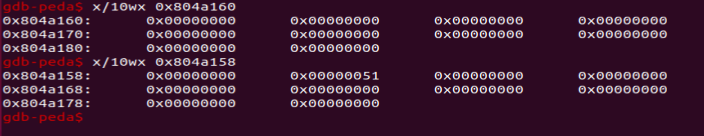
따라서 청크 type, size를 확인하려면 0x8 만큼 빼야 확인이 가능하다.
[그림 1-4]에 0x804a158이 type이고 0x51이 size이다.
size는 헤더 정보를 포함한 크기가 size에 적힌것이다.

malloc를 모두 실행 후 모습이 [그림 1-5]이다.

f -> fp(); 실행하기전 heap를 확인해 보면 argv[1]에 입력했던 AAAA가 들어가 있고 0x804a1b0에는 0x8048478 주소가 들어가 있다. 이 주소는 nowinner 함수의 주소로 추측이 된다.
따라서 argv[1]에서 overflow를 일으켜 0x804a1b0 위치에 winner 주소로 덮어보자.

winner 주소를 찾고 overflow를 일으키면 [그림 1-7] 문자열을 확인할 수 있다.
